AI Use Cases in GRC: An Explorative Guide

If you know the line, “Stories written before space travel but about space travel,” from Philip K Dick’s novel, Do Androids Dream of Electric Sheep (adapted to Ridley Scott’s Blade Runner), you’d agree that it resonates with how we feel about recent AI breakthroughs (both imagined and real). Unlike the theme of this cult classic—technological tensions (driven mainly by AI) and their apocalyptic impact on society, individualism, and humanness are (thankfully) far from reality. With governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) programs and strategies in place, organizations and governments can solve ethical and moral dilemmas concerning AI maturity. In this blog, we will explore the critical AI use cases in GRC.
Outside of the neo-noir but thought-provoking setting of emerging technologies and their inherent risks, AI and GenAI-led tools are mere enablers of complex business operations. A robust GRC framework helps businesses define ethical guidelines and mull the consequences of their corporate, business, and technological choices on society, the environment, and communities.
Traditional AI and GenAI’s automation, data analysis, classification, and content generation (text, images, audio, and video) are longstanding elements for organizational success in the digital era. These technologies also play a critical role in increasing stakeholder and investors’ confidence by transforming GRC workflows with higher accuracy, efficiency, reporting, and decision-making.
However, on the flip side, new threats such as cybersecurity attacks, data breaches, and compliance risks from evolving laws and regulations pressure organizations to reassess the implications of technology, people, and process decisions. That also means looking deeply into the AI in GRC software supporting enterprise GRC software. Mitigating risks in large-scale AI projects and experiments while also leveraging AI’s revolutionary capabilities to support GRC is a vicious cycle to contend with. Oversight and poor judgment resulting in hefty legal fines and reputational damage is the dystopian scenario every organization strives to avoid.
Common AI Use Cases in GRC
In our previous blog, we discussed the technical foundations of IBM Watsonx platform and its role in fostering safe, secure, and trustworthy AI by reducing unintended biases and discrimination. IBM OpenPages with Watson solution has been simplifying GRC objectives for scores of enterprise customers with its unified GRC solution powered by next-gen AI capabilities and data platform built to govern meaningful AI. Last year, the OpenPages Wastonx.governance solution was released as a part of the IBM Cloud for AI governance initiative. The solution helps users design and build AI models based on responsibility, transparency, and trust principles. It makes it easy to scale AI projects and unlock AI use cases for GRC workflows.
In summary, the OpenPages with Watson solution was built to foster ‘AI for AI’ initiatives for organizations across industries and highly regulated spaces like banking, finance, insurance, healthcare, and federal and local government. To understand how AI resolves ethical dilemmas around AI and upholds compliance obligations, we have explored a few common AI use cases in GRC.
- AI for Governance:
Governing activities across an intricate network of data, systems, processes, and teams to foster equity, ethics, economic viability, and environmental protection is the overall premise of governance. GenAI capabilities aid governance activities with the following tasks:
- Reporting & Documentation Automation: GenAI helps reduce manual efforts when creating documents such as governance policies, manuals, guidelines, and board reports by generating documents according to governance standards. The GenAI tools can also automate the building of up-to-date reports by capturing relevant information from disparate sources for reporting purposes.
- Building Governance Policies: Policies and frameworks help organizations and teams gate-keep activities to keep them in line with regulatory and compliance objectives. GenAI tools aid the policy and procedure document creation process by reducing human efforts in prepping governance documents from scratch. Additionally, the intelligent data catalog within the AI-led IBM OpenPages GRC tools leverage a cloud-based metadata repository. The repository allows users to access, curate, categorize, and share data, knowledge assets, and their relationships, wherever they reside, to create policy documents.
- Governance Decision Making: Governance activities require accurate, reliable data for decision-making and planning. GenAI’s underlying analytical capabilities help derive essential insights from scores of data volumes to help governance leaders and teams make informed decisions based on trends, patterns, risk positions, and more.
- Model Risk Governance: Managing data model risks throughout the model lifecycle requires transparency and collaboration of model development teams, owners, validators, and executives. AI capabilities like automation consolidate disparate GRC functions and adhere to model-focused regulations. IBM Watson’s OpenScale helps enterprises to store documentation of AI model validation test results and receive metrics and reports.
- IT Governance: The complexity of enterprise architecture, with several interdependencies and siloed systems, makes it difficult to govern IT projects and applications. AI for IT governance can unlock predictive analytics to flag even the most subtle risk factors and predict future IT regulations so that organizations can prepare for new requirements.
- AI for AI Governance: With the widespread adoption of AI and, recently, GenAI, the need for ethical guardrails emerges as our real-world biases, prejudices, and stereotypes become embedded in AI systems. From global judicial systems to search-engine results, AI decisions that are subject to discrepancies and inserted biases and discriminations fuel global judicial systems.
- The implications of AI tools used for decision-making by legislative and administrative bodies, healthcare companies, education, and financial, and banking systems can widen inequality gaps and threaten fundamental human rights. AI governance tools led by AI capabilities such as the Watsonx.governance now supports AI Anywhere along with powerful GRC features.
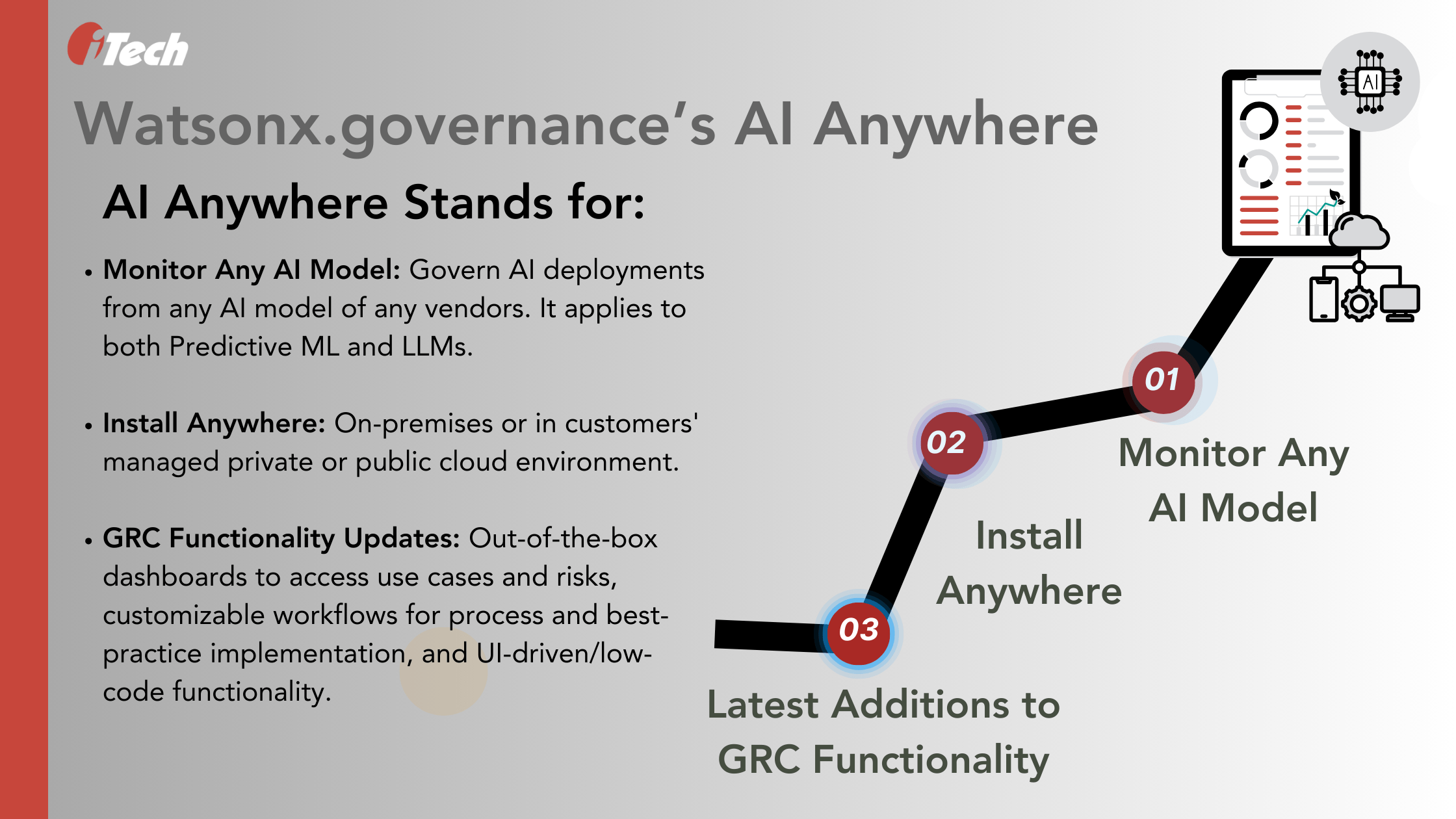
- AI in Risk Management:
An organization’s risk management strategies aim at identifying and mitigating risks while remaining cost-effective and competitive. Risk management is a holistic approach that involves further processes like risk assessments and analyses, risk calculation, and risk treatment and response. Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs), Chief Risk Officers (CROs), and other IT security and risk managers can leverage AI-led tools and capabilities to drive AI use cases in GRC such as:
- Predictive Insights and Analysis: AI’s predictive analytics help identify risk patterns and correlations based on analysis from large volumes of historical data, trends, and other variables. Predictive insights forecast probable risks and defaults while suggesting effective risk mitigation strategies.
- Real-time Risk Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of data sources, operational tasks, daily activities, and cybersecurity incidents helps unlock risks and threats at endpoints, data security, data processing and usage, and other workflows. Identifying risks in real-time gives organizations a sense of control by responding with appropriate control measures on time.
- Fraud Detection: Fraud and anomaly detection by advanced machine learning algorithms are trained to flag unusual patterns, user behaviors, and events to prevent fraudulent transactions and breach incidents that compromise the safety and security of data and its users. This feature is extensively used across banking, financial, retain, and healthcare domains.
- Preventing False Positives: Errors and inaccuracies in data analysis can set off panic mode by suggesting non-existent risks. Organizations can leverage advanced data analytics led by advanced algorithms to accurately analyze sieve through relevant data sets to reveal potential risks and reduce false positive instances.
- Predictive Planning: Organizations can focus on high-priority and high-value items across the business value chain and in their GRC framework. Predictive planning and analysis of past patterns, diverse data sets, and logistics and supply chain operations help prevent wastages or delays. It also helps prepare for unexpected disruptions with judicious resource and time allocation.
- Integrating Risks Management Functions: Siloed risk management functions are counterproductive. AI integration into GRC software can combine risk management activities with relevant stakeholders, policies, and procedures to ensure the organization can react by monitoring its risk stance and comparing it with the latest regulatory frameworks for compliance best practices.
- AI in Compliance:
GenAI use is increasing and driving new risks, and a degree of governance is needed to keep up with the recent laws and regulations. AI automation helps identify and enforce upcoming regulations, enabling organizations to keep up with compliance objectives. Automation helps replace manual, error-driven, time-consuming spreadsheet methods that may lead to misinterpretation and compliance gaps. AI use cases in GRC helps with regulatory compliance in the following ways:
- AI Model Documentation: Organizations can unlock AI capabilities to build and standardize formats that allow consistency to refer and track the model validation processes. It simplifies providing explainable AI results for regulators, auditors, and stakeholders.
- Enhance Quality of Compliance: GenAI systems can review and identify inconsistencies, errors, and discrepancies in compliance documents. It can also help detect outdated, irrelevant language and terminology. It can suggest changes and edits for GRC documents, concepts, and taxonomy to reduce compliance risks.
- Internal Compliance Audits: GenAI can streamline and automate the internal compliance audit procedure. Trained large learning models (LLMs) to review an organization’s internal data and enable audit teams to access specific information and evidence without affecting internal workflow. Automation allows data to be collated from project management tools and systems, helping teams improve the audit process and save time.
- ESG Audits and Compliance: AI helps organizations continuously monitor environmental, social, and governance (ESG) compliance with data analysis of information related to their environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance policies. Using machine learning algorithms, users can understand the latest ESG standards, identify gaps within the current compliance stance, and ensure ongoing compliance.
- Third-party and Vendor-risk Management: AI transforms third-party and vendor-risk management with automation of risk assessment tasks. The advanced machine learning algorithms help monitor important variables such as financial health, cybersecurity practices and policies, and vendor compliance history. Automated risk assessment helps streamline due diligence processes, identify inherent risks, and comply with regulatory standards in vendor relationships.
- Regulatory Change Management: AI-led continuous monitoring and analysis of data from legal databases, government and regulatory announcements, and industry publications help prep for regulatory change management. Natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning algorithms of the AI tools can interpret the regulatory language, identify new updates, and guide organizations with real-time insights into refinements and changes that may impact compliance.
AI Use Cases in GRC: Reality Will Remain Far from Fiction!
At best, Do Androids Dream of Electric Sheep is a cautionary tale with fascinating insights about the farthest that humanity can reach if they ignore (AI) risks beneath the promise. However, with recent incidents of misuse of AI (deepfakes, algorithmic discrimination, cybersecurity threats, privacy breaches, etc.), regulatory and ethical guidelines will go up a notch.
As we anticipate further changes and disruptions in the global regulatory and judiciary framework, organizations can rest their anxieties about the perils of non-compliance or falling behind their GRC goals with OpenPages with Watson.
Connect with our experts for more insights and updates on the implementation of OpenPages to manage your GRC needs with AI enhancements.
