A Guide to Model Risk Governance

The world survived turmoil from geopolitical shifts, soaring inflation, great resignation, and three years of compounding crises from the COVID-19 pandemic. There is no escape for businesses across industries from the state of ‘permacrisis’ or extended periods of instability and insecurity. Most model-reliant businesses in banking, financial services, and insurance (BFSI) are predisposed to intermittent risks and volatility. Chief Risk Officers (CROs) and compliance leaders are tasked to constantly reduce their firm’s risk exposure and manage complex models. Technology platforms for model risk governance, reporting, and compliance are emerging at the forefront to prevent costly mishaps due to model malfunctions or incorrect model usage.
In this blog, we will begin with the basics of models, model risks, and model risk governance in the BFSI space. We will also explore the role of OpenPages Model Risk Governance for enhancing BFSI firms’ overall model risk governance to fulfill long-term governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) goals.
Meaning of Models
Models are quantitative approaches or methods based on economic, statistical, mathematical, or financial assumptions, theories, or techniques. In simpler terms, models convert input data into predictive outcomes. A model can handle data complexity and volume intensity that are manually impossible to process and compute. It includes all the necessary variables and parameters that impact a decision or are integral to making an informed decision. Models serve as cheat codes or decision influencers.
For example, an investment banking or portfolio management company relies on financial models to analyze the performance of various stock portfolios and use them for comparative analysis for profit or loss estimations. The model must include data from income statements, balance sheets, relevant valuation charts, graphs, cash flow statements, mergers and acquisition (M&A) reports, sensitivity analysis, and more, to arrive at necessary outcomes. The financial model also helps investment analysts predict events, internal factors, and macroeconomic trends that impact stock performance, analyze and test different scenarios, plan investment budgets, or allocate resources.
The number and types of models are proliferating in the BFSI space. They are used for evaluating creditworthiness, analyzing business strategies, building due diligence reports, predicting stock valuations, pricing and trading opportunities, asset liquidity management, and more. Firms also incorporate models that are influenced by the regulatory and compliance landscape. According to an in-depth global survey by PwC on model risk management, one-third of the BFSI firms are running more than 100 models. And the number of models in large banking companies is increasing annually by 25%, suggests a leading consulting firm, McKinsey.
Models have further evolved in sophistication with advancements like big data and analytics, and the use of AI and machine learning algorithms to incorporate models beyond traditional use cases. As per the 2023 report of the Risk Management Association (RMA) Survey of Model Risk Management (MRM) practices in banks and financial services firms, 73% of the companies were using AI/ML models in areas like fraud detection, marketing, underwriting, risk modeling, and security.
Understanding Model Risks for Model Risk Management
There have also been several high-profile instances of model-led judgment failures that impacted billions of dollars worth of financial losses and brand reputational damage. A world-leading financial services company adopted a faulty model containing formula and operational errors, which led to risk miscalculation and undervaluation. The incident became a watershed moment in the history of the modern financial crisis, reporting a massive trading loss of billions of dollars. Several other banks also relied on models that failed to predict risks, eventually leading to the 2007-08 global financial recession. In summary, model usage is tied to the risks of adverse consequences from decisions purely based on wrong or misused models or reports.
The flipside of the tempestuous events in 2008 was the introduction of MRM standard by the Federal Reserve Board and the Office of the Comptroller of Currency in 2011 (SR Letter 11-7). The document provides comprehensive MRM guidelines that are widely applicable even to this day. It includes a comprehensive explanation of model risks.
The SR Letter 11-7 explains that model risks are due to fundamental errors or miscalculations in exercises underlying a model. The errors in the model appear anywhere between design and implementation. Risks in models also occur when the models are misused or misapplied. Moreover, models are subject to limitations due to several shortcomings, assumptions about scenarios, uncertainties, and approximations.
According to the MRM standard, using models invariably presents model risks and has a high scope for adverse consequences from decisions made using misused or incorrect model outputs and reports. Even with skilled modeling and robust validation, model risks cannot be ruled out, and banks must treat model risk as any other type of risk.
The MRM guideline was initially created for large banking and insurance companies. Smaller players in the BFSI space soon adopted it. Later, in 2017, the U.S. Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) announced the official adoption of the Supervisory Guidance on MRM with technical conforming changes to extend its applicability to institutions with assets totaling more than a billion dollars.
Model Risk Governance: A Part of the Model Risk Management Framework
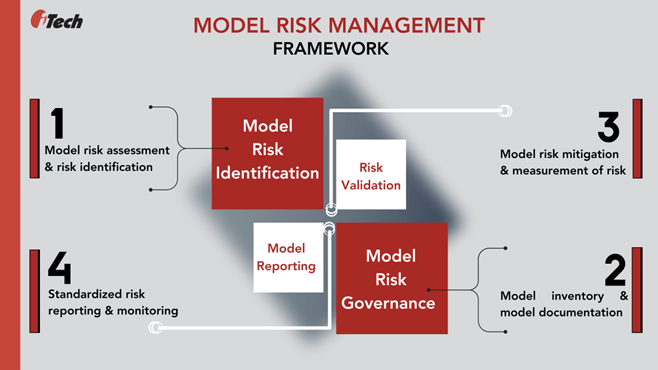
Model risk governance is one of the critical elements of model risk management that provides a robust framework of policies, rules, and a defined set of roles or procedures for clear communication and awareness of model limitations, assumptions, and authority to oversee model usage. The SR Letter 11-7 outlines that building and maintaining strong model governance, policies, and controls is essential for the effectiveness of the model risk framework. Even when the model development, implementation, use, and validation are satisfactory, insufficient model governance can impact the effectiveness of model risk management.
The board of directors and senior managers in banking and financial companies are responsible for implementing a firm-wide model risk management approach. The senior management is responsible for establishing adequate policies, ensuring compliance, allocating staff and resources, making model result evaluations, reviewing validations and audit findings, and taking proactive remedial measures whenever necessary.
Effective model governance requires model inventory and documentation processes.
Model Inventory: Banking and financial firms must create and maintain a complete picture of the models used or developed. Generic guidelines apply for maintaining model inventory like, including the purpose or the products for which the model is designed or intended, along with restrictions on its use. The inventory also specifies if the models are functioning correctly, their latest updates, exceptions to policy, the names of individuals involved in model development and validation, completion dates, and more.
Model Documentation: Maintaining adequate documentation on the model development and validation is important for model risk management and assessments. The documentation comprehensively explains how the model functions, its limitations, and underlying assumptions. It is useful for stakeholders or individuals new to the concept and use of models. Model documentation also provides firms with insights on model-related information for compliance, keeping track of recommendations, and access to various documents, records, and reports for model risk management. For model validation, banks build validation reports articulating reviewed areas, potential deficiencies over a range of economic or financial situations, and concise executive summaries of model validation results.
OpenPages Model Risk Governance Helps Demonstrate Strong Model Risk Management
From Chief Compliance Officers (CCOs), CROs, and C-suite leaders to front-line staff of modern banking and financial space, everyone needs a solution that brings all stakeholders and model risk data together. To address a regulatory need for establishing a clear model risk management framework it requires an elevated level of stakeholder engagement and transparency into the processes. OpenPages Model Risk Governance helps BFSI companies exhibit robust model governance, reporting, and compliance.
The powerful AI capabilities from IBM Watson in the OpenPages platform help integrate disparate GRC systems and risk management functions into one integrated solution, reducing the cost and maintenance of multiple systems and solutions. OpenPages Model Risk Governance solution merges flexible data models with complete document management, powerful workflow capabilities, and business intelligence. By leveraging Watson AI capabilities, users can also develop and scale the use of AI with trust and transparency to build a business-ready analytics foundation to accelerate GRC adoption.
Now let us explore more from the feature overview of the OpenPages Model Risk Governance:
- Model Risk Regulatory Compliance: BFSI companies face strong regulatory pressure on how they create, manage, and utilize financial risk models. The Model Risk Governance module of the OpenPages platform is compliant with model-focused regulations across geographies and jurisdictions. It is cost-effective for businesses as it readily adheres to a wide range of model risk governance and management regulations.
- Comprehensive, Enterprise-wide Model Inventory: The solution provides a highly configurable and customizable platform to maintain model inventory in a way that helps the firm align it with regulator-specific requirements and categories. It helps demonstrate strong financial risk governance.
- Easy to Identify and Document Model Issues and Metrics: BFSI companies can clearly outline all policies and procedures involving the model inception, management, and use. They enable management to review org-wide compliance levels based on the results in the configurable dashboard. The solution also enriches reports from model inventory with features that will allow better issue management, self-assessment of models, and key metric tracking.
- Dynamic Reporting on Model Inventory Management: The solution’s customizable, dynamic dashboards and dimensional reporting provide higher visibility and control to manage model risks and give users clear details into the usage of models and model risks across the enterprise.
- Role-based Model Ownership: Managers can assign tasks to reduce model risks by quickly identifying model owners and stakeholders involved in the development, validation, and vetting of models.
- Financial Risk Governance as a part of GRC Solution: OpenPages Model Risk Governance helps BFSI organizations demonstrate financial risk governance by assisting them to organize and centralize models for measuring and managing financial risks. It helps collate and maintain model reviews and validation data, delegate roles and ownership for model risk management, and report issues in model or model inventory.
- Easy to Manage, Build, and Optimize AI Models: BFSI firms can leverage IBM Watson OpenScale integration within the solution to manage AI model risks, validate AI models, and monitor their production for complete trust and transparency. The OpenScale integration also helps users receive automated metrics and reports, and store AI model validation test results documents.
OpenPages and iTech GRC: A Force Multiplier for Model Risk Governance
The hard lessons about model risks from global brands and renowned BFSI businesses reflect patterns that serve as cautionary points for smaller companies to emulate and assess their preparedness for risks. Two-thirds of firms already use a model risk management solution. As volatility in multiple industries grows in parallel, tools and platforms adopted for model risk governance must be aligned with the latest regulatory and risk management imperatives.
In today’s AI-driven era, businesses can harness AI capabilities to break down the complexities in model building, model risk calculations, and standardizing processes and best practices for model risk governance. The benefits of OpenPages Risk Governance platform and insights of the iTech GRC team converge to empower businesses of every size to prepare for the turbulent days to come. We are interested in helping companies manifest outcomes by understanding risks and strengthening innovations by unlocking the platform’s AI capabilities. Our experts can help embed structural changes to our customers’ risk and compliance processes with the OpenPages’ integrated GRC solution.
We would love to answer your questions on the OpenPages Model Risk Governance platform and the pain points it helps address in banking and financial risk management. Let us schedule a consultation to get you in touch with our GRC experts!
