What is a Third-Party Risk Management Framework?

Nowadays, businesses are more interconnected than ever, relying on a vast network of third-party vendors and partners to drive efficiency and innovation. While these partnerships offer numerous benefits, they expose organizations to many risks, including data breaches, regulatory violations, and reputational damage. These risks are why companies should ensure they have a solid third-party risk management framework in place.
According to research by Gartner, more than 80% of legal and compliance leaders report identifying third-party risks after the initial onboarding and due diligence process. This indicates that traditional due diligence methods in risk management often fail to capture new and evolving risks.
So, what does this mean for your business? Let’s explore the question: Is My Business Liable for Third-Party Data Breaches?
Case 1: Financial Services Industry
The answer is a yes if you operate in the financial services industry. Regulatory bodies in the United States, such as the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC), the Federal Reserve System (FRS), and the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), are clear: the ultimate responsibility lies with your board of directors and senior management to ensure all activities are conducted safely, soundly, and in compliance with the law, even when using third-party services.
The OCC’s risk management guidance states that a bank’s use of third parties increases its obligation to ensure activities are conducted safely and legally. Similarly, the FFIEC emphasizes that third-party providers do not absolve an institution’s board of directors and management of their responsibility.
Case 2: Non-Financial Services
Even if your organization operates outside the United States, if you have a presence or customers in the U.S., you could still be held liable for breaches involving third-party providers. A cautionary tale comes from a non-U.S. multinational company fined $772 million in 2014 for violating the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA). The company’s troubles stemmed from third-party misconduct and inadequate due diligence and corporate controls over them.
In conclusion, the message is clear whether you’re in financial services: thorough oversight of third-party providers is essential to avoid potentially costly breaches and regulatory penalties.
What is a Third-Party Risk Management Framework?
A third-party risk management framework is an organized method for identifying, evaluating, and managing risks connected to third-party partners and vendors. A third-party vendor is any individual or group working independently of an organization that delivers goods, provides services, or performs duties on the firm’s behalf.
A framework for third-party risk management often consists of a collection of rules, practices, policies, and controls intended to assist companies in managing the risks related to third-party suppliers. These frameworks provide a consistent and repeatable approach to managing third-party risks across the organization.
Components of a Third-Party Risk Management Framework
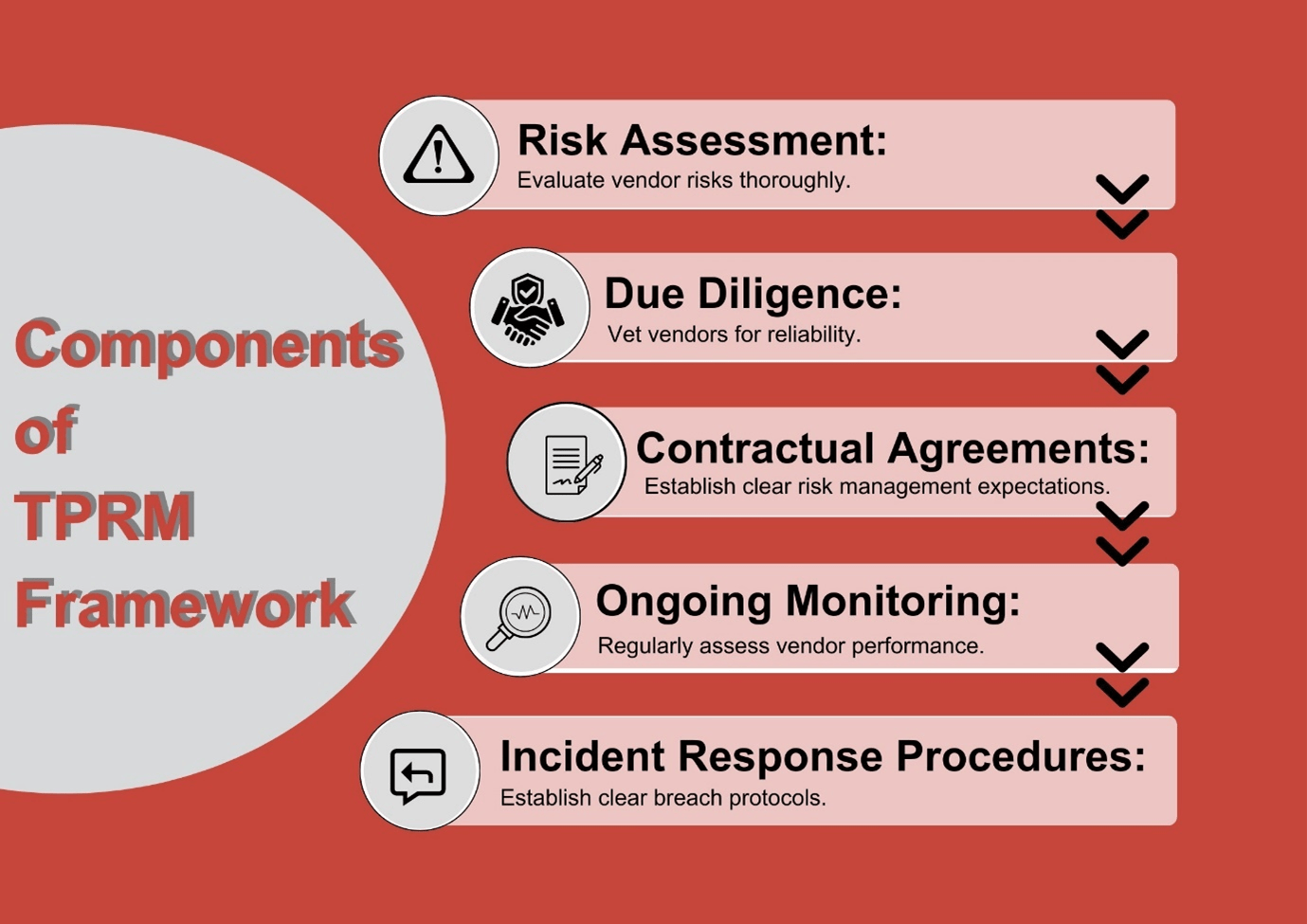
Risk Assessment: One of the critical components of a TPRM framework is risk assessment, which involves evaluating the risks associated with third-party vendors to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities. This step is crucial for understanding the specific risks posed by each vendor and determining the appropriate level of due diligence and oversight required.
Due Diligence: Another critical element of a TPRM framework is due diligence, which involves conducting background checks and reviewing legal documents to assess the vendor’s reliability and suitability. By thoroughly vetting potential partners, businesses can reduce the likelihood of engaging with high-risk vendors and mitigate the possible impact of any breaches or misconduct.
Contractual Agreements: Contractual agreements are also essential in a TPRM framework. They establish expectations, requirements, and obligations related to risk management and clearly outline the responsibilities of both parties regarding data protection, security protocols, and incident response procedures.
Ongoing Monitoring: Ongoing monitoring is another vital aspect of a TPRM framework, as it involves regularly assessing the performance of third-party vendors to ensure that contractual obligations are being met. This step is crucial for identifying any red flags or signs of potential misconduct early on and taking corrective action to mitigate risks.
Incident Response Procedures: Finally, incident response procedures are essential in a TPRM framework, as they establish protocols for responding to security incidents related to third-party vendors. Businesses can minimize the impact on their operations and reputation by having a clear plan for addressing breaches or other security incidents.
Creating a Third-Party Risk Management Framework: Step by Step
Organizations that engage external partners and vendors to provide goods and services must establish a comprehensive third-party risk management system. This framework should encompass all aspects of managing third-party risks, including identification, evaluation, mitigation, and ongoing monitoring.
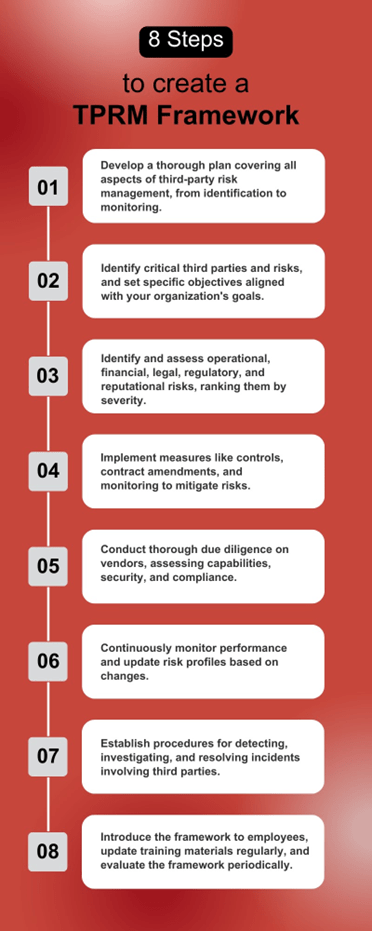
The process for developing a third-party risk management framework typically involves the following steps:
- Establish a Comprehensive Framework: Develop a thorough framework covering all aspects of third-party risk management, including identification, evaluation, mitigation, and monitoring.
- Define Scope and Objectives: Determine the scope by identifying critical third parties, relationships, and risks. Establish specific objectives aligned with the organization’s overall risk management strategy and operational goals.
- Risk Identification and Assessment: Identify operational, financial, legal, regulatory, and reputational risks associated with third-party partnerships. Assess risks based on likelihood and potential impact, ranking them by severity.
- Risk Control and Mitigation: Implement measures to mitigate risks, such as controls, contract amendments, and risk management provisions. Ensure appropriate safeguards are in place to monitor and track third-party performance.
- Due Diligence and Vendor Selection: Conduct thorough due diligence on prospective third parties, assessing capabilities, security posture, compliance, and financial stability. Select vendors aligned with the organization’s risk tolerance and performance requirements.
- Monitoring and Performance Evaluation: Continuously monitor third-party performance and contractual compliance. Regularly review and update risk profiles based on changes in risk appetite or the third party’s risk environment.
- Incident Management and Reporting: Establish procedures for reporting and addressing incidents involving third parties. Promptly detect, investigate, and resolve events, sharing relevant information with stakeholders.
- Training, Awareness, and Continuous Improvement: Introduce the framework, policies, and procedures to employees and stakeholders. Update training materials regularly to reflect changes in the risk environment, legal requirements, and industry standards. Periodically evaluate and update the framework to ensure effectiveness and alignment with organizational goals.
Benefits of a Third-Party Risk Management Framework
Implementing a third-party risk management (TPRM) framework offers numerous advantages for organizations:
- Improved Risk Awareness: A TPRM framework enhances understanding of risks associated with third-party vendors, enabling informed decision-making and proactive risk mitigation.
- Enhanced Risk Management: The framework provides a systematic approach to identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks, facilitating effective risk reduction or elimination measures.
- Increased Regulatory Compliance: Many industries require third-party risk management to comply with regulations, helping organizations avoid legal or regulatory penalties.
- Protection of Sensitive Data: A TPRM framework ensures that vendors and partners handle sensitive data securely, reducing the risk of data breaches.
- Better Vendor Relationships: Implementing a TPRM framework fosters strong, safe, and trustworthy supplier relationships, improving service delivery and performance.
- Reduced Financial Losses: Organizations can minimize the financial impact of potential risks and losses by mitigating third-party risks.
- Improved Reputation: Effective TPRM frameworks help prevent data breaches and protect customer information, safeguarding an organization’s reputation.
Choose IBM OpenPages Third-party Risk Management (TPRM)
IBM OpenPages Third-party Risk Management (TPRM) is ideal for managing vendor risks. Here’s why:
- Protect Confidential Information: IBM OpenPages TPRM helps protect confidential information shared with vendors, reducing disruption to compliance, brand, and operations.
- Centralized Risk Repository: It creates a centralized repository of third-party risks, including controls, KRIs, locations, and regulations, providing a holistic view of risks.
- Incident Investigation: The solution enables systematic investigation of vendor risks, enhancing collaboration for corrective actions and real-time visibility into issues.
- Third-Party Questionnaires: These streamline and standardize vendor risk surveys and questionnaires, helping qualify vendors based on assessment scores.
- Third-Party Integrations: IBM OpenPages TPRM integrates with SecurityScorecard for IT security benchmark scores and Shared Assessments for SIG Questionnaires, eliminating the need for time-consuming vendor assessments.
Are you eager to tap into IBM OpenPages’ AI capabilities for your GRC needs? Reach out to us. Our team of GRC experts is ready to ensure you maximize the potential of IBM OpenPages. As a committed IBM RegTech partner, we specialize in selling and implementing IBM OpenPages with Watson.
