What is a Third-Party Risk Assessment?

In today’s modern world, businesses rely increasingly on third-party vendors and partners. This collaboration brings incredible benefits but has a hidden cost: increased cybersecurity risks.
Think about it: how many third-party tools and services do you use daily, personally, and professionally? Now imagine that number multiplied by hundreds, even thousands, for larger organizations.
Here’s the alarming part:
- 60% of security incidents are estimated to stem directly from third-party vulnerabilities.
- Over 60% of organizations manage over 1,000 third parties, which keeps growing as systems become more complex.
- Nearly half (48%) of organizations need help to track and manage their third-party risk effectively.
- Only 40% of organizations feel confident they fully understand their third-party cyber and privacy risks.
The above statistics highlight the impact, complexity, challenges, and knowledge gap surrounding third-party risk assessment.
What is a Third-Party Risk Assessment?
A third-party risk assessment evaluates the potential risks to your organization by third parties, such as vendors, suppliers, or partners. These assessments are essential because external relationships can expose your business to cybersecurity threats and compliance risks. Non-compliant vendors can disrupt your operations and damage your brand. Additionally, as third parties evolve through mergers, acquisitions, or new capabilities, the risks they pose can also change.

Third-party vendors and partners can introduce many risks that a thorough Third-Party Risk Assessment (TPRA) helps identify and mitigate. Let’s dive into the key reasons why TPRAs are essential:
- Cybersecurity Protection: External partnerships can expose your organization to cybersecurity threats like data breaches and cyber-attacks. For example, Target experienced a massive data breach due to a vulnerability, compromising the data of millions of customers.
- Compliance Assurance: Non-compliant vendors can disrupt operations and lead to regulatory fines and penalties. For example, Google was fined €50 million by the French data protection authority for violating GDPR.
- Operational Continuity: Third-party disruptions, such as supplier failures or service outages, can impact your organization’s operations. For example, in 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic caused supply chain disruptions worldwide, affecting businesses that relied on third-party suppliers.
- Brand Reputation: Third-party actions or behavior can impact your organization’s reputation. For example, Uber faced backlash and a loss of customers due to a data breach and subsequent cover-up involving a third-party vendor.
How often should Third-Party Risk Assessments be conducted?
The frequency of third-party risk assessments depends on various factors, including the nature of the relationship, the level of risk involved, and regulatory requirements. However, it is generally recommended to conduct third-party risk assessments:
- Periodically: Regular assessments should be conducted at predefined intervals to ensure risks are continuously monitored and managed. The frequency can vary based on the risk level and the third-party relationship’s criticality.
- Upon Onboarding: A thorough risk assessment should be conducted when onboarding a new third party to assess the initial risk exposure and establish a baseline for ongoing monitoring.
- Upon Significant Changes: Assessments should also be conducted when significant changes occur in the relationship or the third party’s operations, such as mergers, acquisitions, or service changes.
- Based on Risk Profiles: High-risk third parties may require more frequent assessments, while lower-risk third parties may be assessed less frequently.
- Regulatory Requirements: Some regulations and standards may require specific assessment frequencies. Organizations should ensure compliance with these requirements.
What are the different types of Third-Party Risk Assessments?
Effective third-party risk management requires going beyond a one-size-fits-all approach. Different types of assessments cater to specific risk areas, providing a comprehensive understanding of potential vulnerabilities:
- Vendor Risk Assessment: Evaluates the risks associated with using a particular vendor or supplier. It involves assessing factors such as financial stability, security practices, and regulatory compliance of the vendor.
- Contractual Risk Assessment: Focuses on assessing the risks outlined in the contracts with third parties. This includes reviewing contract terms related to liability, indemnification, data protection, and compliance requirements.
- Security Risk Assessment: This process assesses third parties’ security posture, including their IT systems, data protection measures, and vulnerability management practices.
- Compliance Risk Assessment: Evaluates the extent to which third parties comply with relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards. This includes assessing data privacy, security, and regulatory compliance risks.
- Reputational Risk Assessment: Assesses the potential impact on the organization’s reputation due to the actions or behavior of third parties. This includes evaluating ethical standards, social responsibility, and public perception.
- Operational Risk Assessment: This evaluates the risks associated with third-party operational activities. It includes business continuity planning, disaster recovery, and service delivery capabilities.
Need an expert IBM OpenPages implementation partner to help you develop a comprehensive GRC solution?
Our certified consultants can assist you in making the most out of IBM OpenPages to achieve your GRC goals now and in the future.
How do we perform Third-Party Risk Assessments?
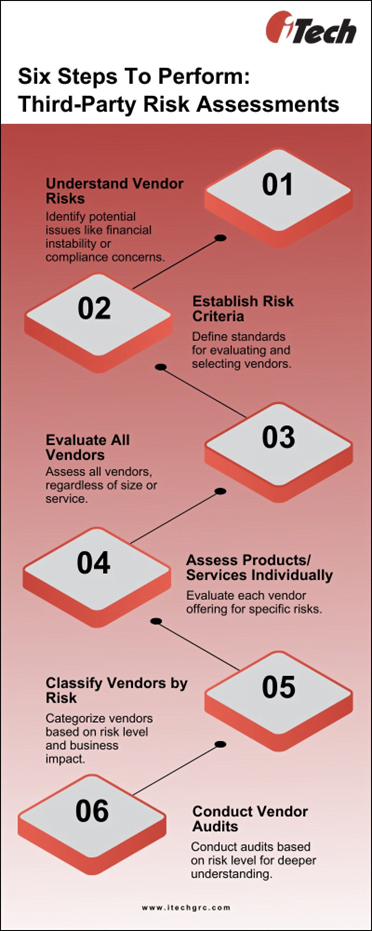
Step 1: Understand the Types of Vendor Risks
When evaluating third parties, it’s crucial to grasp the risks of working with external vendors as ignorance of these risks has catastrophic consequences for your business. Here are some key risks to consider:
- Financial Risk: Assess the vendor’s financial stability to ensure they can fulfill their obligations.
- Compliance Risk: Determine if the vendor complies with current laws and regulations relevant to your industry.
- Subsequential Risk: Evaluate if the vendor uses third parties for processes that could impact your company.
- Resource Risk: Ensure the vendor has adequate resources to deliver the products or services you require.
- Replacement Risk: Consider how easy it would be to replace the vendor if they could not continue operations.
- Reputational Risk: Evaluate how working with the vendor could affect your company’s reputation internally and externally.
While not all risks may apply to your business or the specific vendor, it’s essential to understand and consider them during the evaluation process.
Step 2: Establish Risk Criteria
After understanding the risks, develop risk criteria for third-party assessments. These criteria will vary based on your business type and the vendor’s nature. Regularly assess vendors to avoid bias and ensure you select the right ones. Use a standardized vendor risk assessment format with scoring criteria for each evaluation.
Step 3: Evaluate All Vendors
Don’t limit third-party risk assessments to supply chains and software. Before entering a partnership, evaluate every vendor, regardless of size or the services/products they offer. Even seemingly small vendors like janitorial services can pose a threat if they have access to your data or physical space.
Step 4: Assess Each Product and Service
Conduct two types of assessments: one focused on the vendor and another for each product or service you plan to purchase. Evaluate the vendor’s overall risk to your company, considering factors like reputation, compliance, and customer service. Also, assess each product or service for safety, ease of use, cost, and compliance with laws.
Step 5: Classify Vendors by Risk Level
After assessing a vendor, categorize them based on risk level (high, medium, low). Also, assign a business impact score to determine the importance of the vendor and their offerings to your organization. This classification helps streamline risk management and ensures consistent, unbiased evaluation.
Step 6: Conduct Vendor Audits
Audit vendors based on their risk level and independent reviews. Consider scheduling onsite visits, especially for high-risk vendors, to better understand their operations and mitigate potential risks.
Following these steps, you can effectively assess vendor risks and make informed decisions to protect your business.
What are the common challenges faced in Third-Party Risk Assessments?
Third-party risk assessments pose several challenges for organizations. Some of the common challenges include:
- Limited Visibility: Organizations often need more visibility into their third-party vendors’ practices and security measures, making it difficult to assess and mitigate risks effectively.
- Resource Constraints: Conducting thorough third-party risk assessments requires time, expertise, and resources. Many organizations need help with resource constraints, leading to incomplete or inadequate evaluations.
- Complexity of Relationships: Third-party relationships can be complex, involving multiple vendors and subcontractors. Managing and assessing the risks associated with these relationships can be challenging.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting regulatory requirements related to third-party risk management, such as GDPR or HIPAA, adds complexity to the assessment process.
- Data Security: Ensuring the security of sensitive data shared with third parties is a significant challenge. Organizations need to assess how third parties handle and protect this data.
- Vendor Reluctance: Some vendors may be reluctant to provide detailed information about their security practices, making it challenging to assess their risks accurately.
- Dynamic Environment: The business environment constantly evolves, with new risks emerging regularly. Organizations need to monitor and assess third-party risks to stay ahead continuously.
- Lack of Standardization: Third-party risk assessment practices need to be more standardized, making it challenging to compare and benchmark assessments across vendors.
Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach to third-party risk management, including robust assessment processes, clear vendor communication, and ongoing monitoring of third-party relationships.
What are the best practices for managing Third-Party Risk Assessment?
To perform third-party risk assessments effectively, consider the following best practices:
- Measure Assessment Effectiveness: Continuously monitor the accuracy of assessments using clear success indicators aligned with your goals. Annual assessments are crucial for identifying and addressing risks.
- Utilize Technology: Leverage technology to streamline assessment processes. Use a central platform to monitor all suppliers, update assessment scopes for new vendors, and incorporate risk information for decision-making.
How can organizations automate Third-Party Risk Assessments?
The short answer is to utilize third party risk software solutions such as IBM OpenPages.
Organizations can enhance third-party risk assessment processes by leveraging software like IBM OpenPages. This platform offers various automation features that streamline assessments and bolster risk management capabilities:
- Automated Risk Scoring: This system automatically evaluates and scores third-party risks based on predefined criteria, enabling the prioritization of high-risk vendors.
- Workflow Automation: Automates task assignments, notifications, and approvals, ensuring assessments are conducted efficiently and consistently.
- Data Collection Automation: Streamlines data collection from third parties, reducing manual efforts and ensuring information accuracy and completeness.
- Reporting and Dashboards: Provides automated reports and dashboards to track assessment status, monitor key metrics, and communicate findings to stakeholders.
- Integration with Third-Party Systems: Integrates with other systems, such as vendor management platforms and risk intelligence tools, to automate data exchange and enhance assessment efficiency.
IBM OpenPages for Third-Party Risk Management leverages automation to improve assessment effectiveness, efficiency, and scalability.
