The Allure of Healthcare Data: Why is it a Hotbed for Healthcare Cybersecurity Breaches?

Digital health systems and data-driven medical devices enhance performance and care quality in the healthcare industry. However, converting large volumes of personal health data into digital formats for storage and usage introduces several privacy and data security concerns. Healthcare data such as patient information, clinical observations, payment details, prescriptions and treatment records, and personally identifiable information (PII) are targeted for cybersecurity extortions and are highly profitable on the dark web.
In the first half of 2024, the Department of Health and Human Services reported recording nearly 341 major breaches. Ten of the most significant breaches impacted more than 31 million individuals in the U.S. Let’s review some recent high-profile cybercriminal activities in the healthcare industry. In the later part of the blog, we will also examine factors that make the healthcare industry a prime target for hackers and cybercriminals.
Four Largest Healthcare Cybersecurity Breaches in 2024
1. Change Healthcare’s Ransomware Attack :Change Healthcare, one of the largest payments and revenue cycle management providers became aware of a ransomware attack on February 21st, 2024. Within a month, the company confirmed that a sizeable part of the healthcare data was leaked into the dark web despite its parent company, UnitedHealth, paying a ransom of $22 million in Bitcoin.
Upon investigations, Change Healthcare found that a particular remote access portal wasn’t using multi-factor authentication (MFA), which led to the data breach impacting nearly a third of Americans.
2. Ascension’s Breach from a Malicious File Download
On May 4th, 2024, Ascension, an emergency care provider’s healthcare workers lost access to patient medical records because of ransomware attacks and were forced to use manual paperwork to communicate and monitor across the healthcare continuum. The care provider announced that accidentally downloaded files by an Ascension employee caused the attack, allowing cybercriminals to steal files from seven servers and lock users off electronic healthcare records (EHR) and other clinical systems.
Ascension’s attack impacted patient care by diverting ambulances and disrupting other clinical touchpoints in hospitals and clinics that relied on the system.
3. Kaiser Permanente’s Breach of 13.4 million Records
California-based U.S. health conglomerate Kaiser Permanente apologized to nearly 13.4 million members who accessed its website and mobile applications for inadvertently sharing their searches with Google and other search engines. So far, there hasn’t been any proof of misuse of that information.
4. Concentra Health Services Breach from Third-party, PJ&A
The Texas-based occupational healthcare leader Concentra encountered a cybersecurity attack through its transcription services provider, PJ&A, affecting almost 9 million patients. The incident is recorded in the Department of Health and Human Service Provider (HHS) Office for Civil Rights (OCR). In January 2024, Concentra confirmed that the patient’s health information compromised from the third-party breach totaled at least 14 million.
Understanding the Reasons behind Frequent Healthcare Cybersecurity Breaches
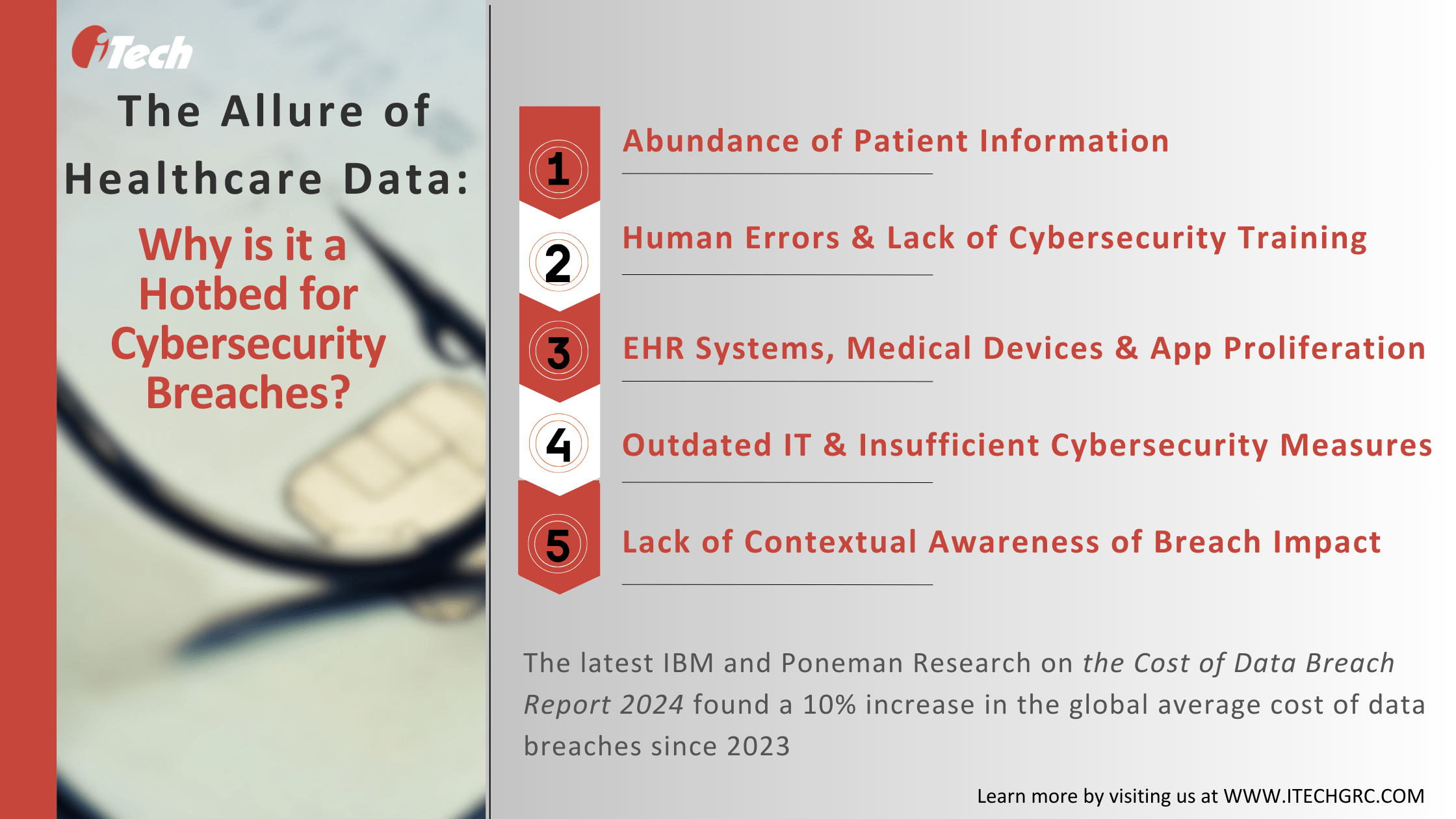
As we approach the last quarter of 2024, it is important to reflect on these data protection failures to maintain patient confidentiality and information privacy while adhering to the latest compliance standards. Here’s a list of reasons healthcare IT systems is vulnerable to breaches and ransomware.
1. All Eyes on Personal Data: Healthcare IT systems and applications are a gold mine of patient data. The centralized architecture of IT systems facilitates seamless collaboration between departments, medical staff, patients, and care providers, making hacking simple. Ransomware groups are also evolving at the speed of innovation and deploying aggressive tactics like zero-day, one-day vulnerability abuse and multiple extortion strategies. According to Akamai’s State of the Internet report, there have been concerning trends in ransomware, with a 39% jump in the number of victims in the healthcare industry.
Access to data through breaches, compromises, and exposure increases the risk of identity theft, insurance fraud, counterfeiting medical records and prescriptions, and other crimes.
2. The Human Element: Vulnerabilities also stem from human errors, insufficient staffing, lack of comprehensive cybersecurity policies, and training on best practices for preventing risks. Lessons from Change Healthcare’s ransomware emphasize the importance of implementing safeguards like MFAs, which cost less than paying hefty ransoms. Compromised user devices can be hacked via the network. To prevent these attacks, organizations must consider risk-based authentication (RBA) solutions that flag the security teams about unsafe devices and prevent users from accessing sensitive data.
With the shrinking labor market, the burden and task overkill on healthcare staff can make cybersecurity an afterthought. Therefore, companies must work towards aligning security practices with IT solutions by implementing frictionless authorization layers like MFAs and single sign-on (SSOs).
3. Medical Devices are Doorways for Cybercriminal Attacks: Healthcare businesses thrive on medical devices and applications connected to their networks to share and access massive amounts of patient data. There are also issues related to managing legacy IT systems and multiple mobile devices that house time-critical medical and patient information. In most cases, users access the data remotely over their devices, which may be unpatched, providing an easy gateway for hackers and cybercriminals to access or steal data and hijack systems.
4. Outdated and Inadequate IT Security: Legacy IT systems usually must be more compatible with recent cybersecurity standards and protocols. They may also need more support for frequent updates. Coupled with insufficient network security, such as unprotected Wi-fi networks and poorly configured security firewalls, unauthorized users can access the systems. Another issue commonly identified from IT audits in healthcare companies is unpatched software, which opens the door to hackers stealing data or spreading malicious viruses.
5. Lack of Contextual Awareness on Breach Impact: The extent to which an organization contextualizes its data protection practices, cybersecurity and IT risk management, and compliance policies matters in the healthcare industry. Multiple stakeholders, such as clinicians, nurses, residents, IT managers, and administrative staff, have varying understandings of the use and limitations of EHR systems and other applications.
Moreover, the complexities are unique to the regulations governing specific IT systems, user groups, and types of data assets exchanged. Therefore, setting up data protection practices requires strong consideration of the context of practice and use. That also requires conducting a context-specific investigation into current knowledge of healthcare data breaches to educate stakeholders across the value chain about breach types, facilitators, and impacts.
Rising Cost is a Major Catalyst for Cybersecurity Action: Explore iTech GRC
The latest IBM and Poneman Research on the Cost of Data Breach Report 2024 found a 10% increase in the global average cost of data breaches since 2023. Nearly one in every three incidents involving shadow data attributed these breaches to mushrooming data volumes, which makes it harder to monitor and prevent risks. Healthcare breaches are the costliest, amounting to $10.93 million last year. Let’s not forget the additional cost to switch to alternative systems and infrastructure to carry out electronic transactions without operational disruptions. Aftermath of Change Healthcare cybersecurity attack is a useful case in point to understand the ripple effects of the disruption—36% claims payment suspension, 80% loss of revenue from unpaid claims, 39% unable to obtain remittance advice, etc.
Whether it is on-prem systems or public and private clouds, attackers are known to find their way across multi-environments to orchestrate attacks. The adoption of security AI and automation reduces the average breach cost by saving nearly $2.22 million. Additionally, research findings suggest that proactive integration of security during the software development lifecycle can help save almost $250,000. Employee training and incident response planning and testing can add up to an average savings of $230,000 and $241,000, respectively.
Explore iTech GRC’s managed GRC services and expertise for implementing IBM OpenPages with Watson and updating IT Governance, Data Privacy Management, and Internal Audit Management modules.
Read how iTech GRC’s certified GRC team helped a leading Cancer Research Institute manage the risks associated with their internal legacy IT systems and third-party vendors.
Are you looking for iTech’s GRC advisory and consultation services to plan your risk and compliance roadmap for 2024? Connect with our experts today!
