FDIC Risk Review 2024: A Nuanced Approach to Risk for U.S. Community Banks

Rising interest rates and an uptick in liabilities drive banking and financial institutions into liquidity risks. We have witnessed the repercussions of misaligned liquid asset portfolios and funding resources, leading banks into epic insolvencies and meltdowns. Federal agencies issued regulatory updates to tighten lending functions. They increased the asset reserves threshold to prevent another sorry state since the Silicon Valley Bank (SVB), Signature Bank, and the New York Community Bancorp Inc. (NYBC) controversy. Banking leaders are immersed in approaching regulatory proposals towards capital, liquidity, and risk management. But there’s more to do to redefine banking business models to prevent liquidity and funding risks.
The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) recently issued a comprehensive risk review report to identify risks and trends likely to affect U.S. banking structure and financial soundness.
iTech GRC empowers enterprises to respond confidently to dynamic operational risks. Our certified risk consultants function as extended teams to ensure that your firm’s risk management and compliance journey is not chaotic. We are solution providers, partners, and ardent observers of the risk landscape. We help enterprises stay updated by leveraging iTech’s advisory and OpenPages with Watson implementation services.
Here’s the update on the annual FDIC risk review of the U.S. banking sector.
2024’s FDIC Risk Review: Broader Risk Categorization
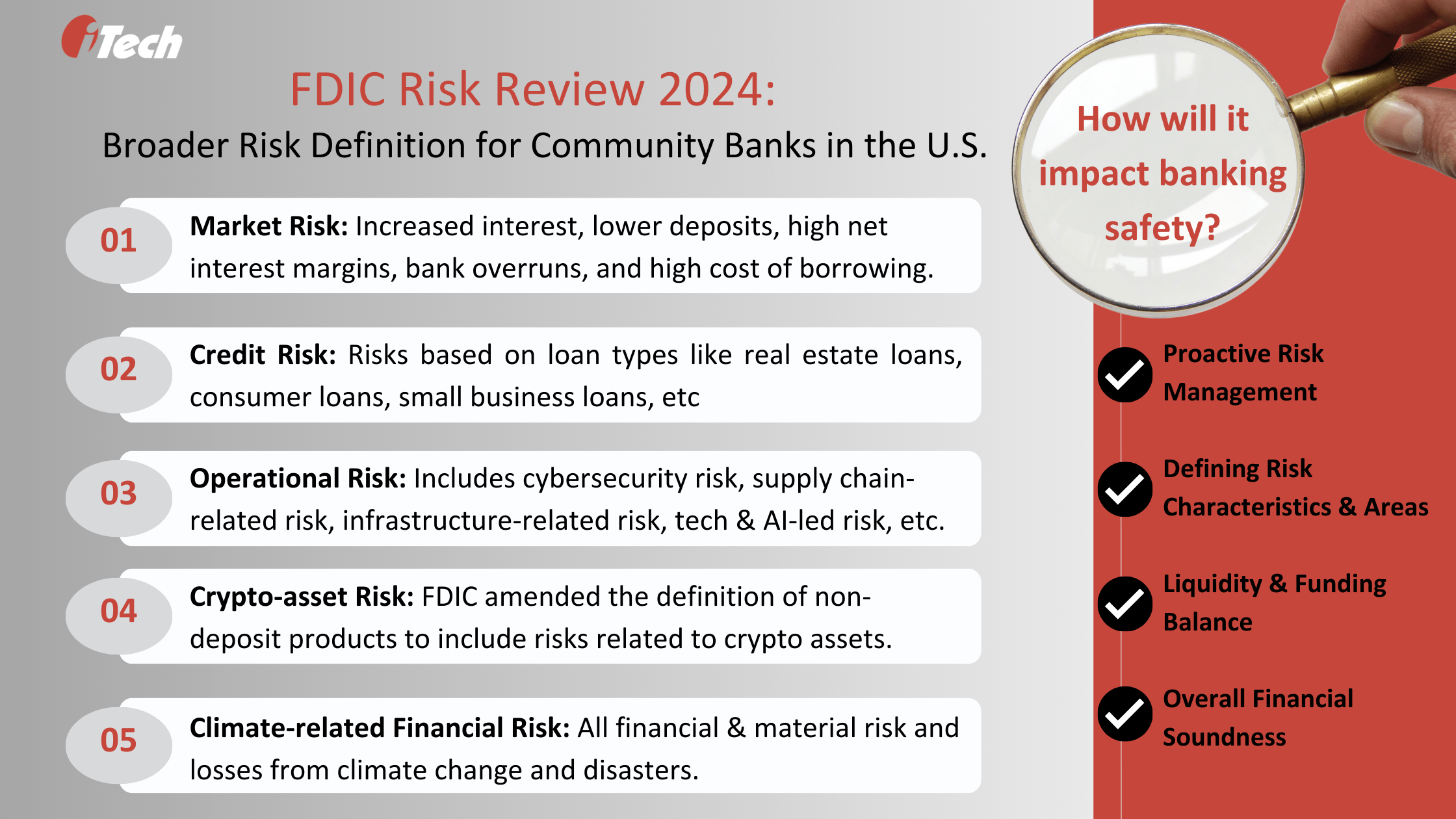
The agency summarized risks affecting U.S. banking into five major categories: market risk, credit risk, operational risk, crypto-asset risk, and climate-related financial risk.
- Market Risk: Market risk underscores factors like liquidity risks from increased interest rates, lower deposits, high funding costs, and higher net interest margins. During 2023, many U.S. banks endured several market risks that impacted their liquidity positions. Reduced bank deposits and a shift towards higher-yielding deposit accounts increased the cost of funding and interest expenses. As a result, several banks depleted their securities to fund deposit outflows, pledged them for liquidity, and turned to higher-cost borrowing to manage their foreseeable liquidity requirements.
- Credit Risk: The FDIC classified credit risks by loan types, such as commercial and residential real estate loans, consumer loans, agriculture loans, small business and corporate debt, nonbank loans, and loans to energy companies. In 2023, commercial estate loans and consumer loan areas demonstrated asset quality deterioration.
- Operational Risk: By operational risks, FDIC refers to the risk probabilities from banking activities. They include cybersecurity incidents like ransomware, which is becoming more sophisticated, supply chain attacks, and infrastructure risks from adopting quantum computing and GenAI. These risks continue to affect banking institutions and their third-party vendors. The report also found that the operational risks from check frauds surged despite the decline in check usage.
- Crypto-asset Risk: Even though crypto-assets-related transactions are limited in the U.S., it has a high-risk probability for the banking ecosystem. The risk complexity amplifies the challenge of monitoring or assessing them. The FDIC and a few other federal banking agencies decided in 2023 to closely monitor the crypto-asset-related activities of banking companies. The agency also issued an amended definition of ‘non-deposit product’ to include crypto assets.
- Climate-related Financial Risk: Last year, climate-related disasters were rated at an all-time high since 1980, costing billions worth in losses! Insurance policies include coverage for some or all of those losses, but the cost of weather-related disasters and events is increasing, impacting banking companies’ financial risks. Some of those policies are increasingly becoming expensive or unavailable.
FDIC & OCC on Risk Review & Monitoring
The broader definition of risks in the banking domain involves assigning characteristics to various risk factors. This would enable banking and financial firms using different business and financial models to keep a close eye on risks that can have far-reaching implications after interacting with existing banking vulnerabilities. Banking customers and investors are interested in liquidity and overall financial soundness.
In 2024, higher interest rates, aggressive regulatory compliance, GenAI convergence, decarbonization pressures, increased risk of fraud and security threats, geopolitical events, and reduced money supply chains are redefining the banking architecture. The FDIC 2024 risk review particularly targets community banks with an overarching goal of monitoring their risk areas.
The Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC) also issued its Semiannual Risk Perspective for Spring 2024, covering key risks in the federal banking system, savings associations, and agencies. The OCC reported that banks must identify material risks and their connected impact. It identified the key credit, market, operational, and compliance risk themes. The OCC also stressed the importance of continuous risk management to alert banks against complacency and adopt enterprise-wide resilience activities that concurrently impact multiple risk categories.
An Optimistic Outlook Despite Volatility & High Interest
Even after great turmoil during the initial part of 2023, the U.S. banking sector demonstrated stable liquidity and asset quality metrics. The FDIC also reported that by the end of the year, problem banks accounted for only 1.1% of banks, indicating that they were ‘near the low end of the typical range for non-crisis periods.”
Moreover, consumer and government spending drove economic growth despite high interest rates, a slowing labor market, and bank stock underperformance due to SVB’s liquidity and funding crisis.
Explore the IBM OpenPages with Watson for Banking Risk Management
At iTech, we have helped several banking enterprises explore IBM’s AI-driven, unified GRC platform, IBM OpenPages with Watson, and its advantage in managing and monitoring advancing risks. As a trusted OpenPages implementation partner, we have witnessed our GRC experts assisting our clients to unlock the below benefits to ace their risk management objectives:
- Centralized Risk Management Functions: OpenPages implementation success is directly tied to breaking down the silos across the risk management areas and achieving a single pane of view of risk and regulatory obligations.
- Risk and Control Assessments: OpenPages capabilities extend beyond risk identification. Your enterprise can conduct operational risk and control assessments, build mitigation plans, and continuously monitor the impact of control measures. Configurable dashboards also help detect risk items and keep track of risk inventory.
- Intuitive Regulatory Management: With built-in regulatory compliance manager dashboards, keep track of the regulatory pulse, workflows, interactions, changes, and compliance assessments.
- Risk Audit Scoping and Planning: Audit manager dashboards will provide an overview of the key audit areas to focus on.
- Configure, Deploy, and Maintain Workflows: Leverage the administrator to make OpenPages deployment seamless and set user access. The intuitive user guidance and interactive design enable a consolidated view of the tasks, enhancing the overall user experience of the platform.
- High Scalability: The extensible and fully configurable OpenPages platform helps scale to accommodate tens to thousands of users.
- Uncover Open, Trusted, and Ethical AI Usage: IBM watsonx ™ AI and data platform helps eliminate risks that inhibit the roll-out of AI applications. Built on IBM’s principles of trust, the platform helps enhance the value impact of AI and AI workflows using trusted data sources.
- AI Model Risk Governance: Readily govern GenAI and machine learning (ML) models for accuracy, model health, model metadata, drift bias, and quality across the lifecycle with IBM watson.governance.
- Frictionless Contact Center Support: The conversational AI solution, watsonx Assistant, helps empower broader users, including non-technical users, to build and configure the seamless self-service interface and GenAI voice assistants. It helps deliver digital and automated banking and responsive customer service, enhancing productivity and cost savings.
Are you looking for a dedicated GRC partner certified in IBM OpenPages to manage risks and reduce the cost of compliance?
Contact our team to learn more about iTech GRC services.
