Bank Regulation and Supervision Increases in 2024: Regulators Announce New Proposals
2023 was indeed a poster year for disruptions. Evolving bank regulations and supervision will drive banking and financial services firms to tread consciously in 2024.
Let’s explore the latest banking and supervisory regulations impacting banking and financial institutions’ governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) agenda this year.
Basel III Endgame:
Post the 2009 financial catastrophe, global financial regulators reached a collective consensus on building measures that set minimum capital, risk, and liquidity requirements for large banking institutions. Basel was initiated by a syndicate of central banks from 28 nations called the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision.
Following last year’s Silicon Valley Bank crisis, regulators urged standards revisions to make the banking sector more risk-resilient and to re-instill investors and the public’s confidence in banking systems. The Group of Central Bank Governors and Heads of Supervision Chair Mario Draghi, the committee’s Supervision Chair Stefan Ingves, and the Secretary General William Coen, announced the finalization of Basel III reform in 2017. The endgame proposal is the committee’s final response to the global financial crisis.
Basel III framework aims to improve large bank regulation and supervision, and risk management activities. Below are some of high-level updates to the Basel III Endgame:
1. Banks with assets totaling $100+ billion (the previous requirement was $250 billion) must increase their reserves or maintain a minimum amount in long-term debt.
2. The minimum amount of long-term debt must be:
- Equal to more than 6% of risk-weighted assets,
- or 3.5% of average total assets
- and 2.5% of total leverage exposure under said ratio for banks for which supplementary leverage ratio may apply.
3. Higher financial leverage ratios for global systematic important banks (G-SIBs).
4. New liquidity coverage ratio where banks maintain sufficient high-quality assets (HQLA) reserves and net stable funding (NSF) ratio of at least 100% to pay off outstanding maturities and risk levels of assets.
The Basel III Endgame proposal will be consequential to financial and economic health by slowing down lending to ensure banks have enough capital to sustain themselves during recessions and attract safer investments in the long run. While Basel III targets large banking firms, the regulations will impact small and medium-sized banks with higher operational costs.
Additionally, nonbanking financial companies (NBFCs) such as fintech, digital payment companies, and big tech firms must also prepare to keep up with regulatory updates. Many banks have requested time to comprehend and comment on the proposal. Basel III will take effect on July 1, 2025, along with a three-year phase-in period to help banks accommodate to the new changes.
Higher Scrutiny for Banks Mergers Over $100 Bn:
On March 21, 2024, the U.S. Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation’s (FDIC) board of directors issued a proposal to increase scrutiny of banking mergers that can result in more than $100+ billion in assets. The draft proposals include principle statements rather than procedural guidelines to prevent banking failures resulting from mergers and acquisitions. The new proposal sparked outrage from financial reform advocates who condemned the regulation for allowing some of the largest banking mergers like the New York Community Bank (NYCB.N) with the Flagstar Bank (FBCANK.UL) of Michigan and JPMorgan Chase & Co’s (JPM.N) acquiring of First Republic Bank (FRCB.PK).
Stress Testing Exercise for Banks:
Federal agencies (includes the Federal Reserve Bank (FRD), the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), and the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC)) introduced the stress testing for banks to assess their ability to resist hypothetical recession scenarios. The test requirements apply to 32 leading banks in the U.S. to measure their risk resilience against the mounting costs affecting corporate lending and commercial and residential real estate.
The new stress tests are in response to last year’s three notable banking failures—Silicon Valley Bank, New York Community Bancorp Inc. (NYCB)’s bankruptcy following its Flagstar Bank acquisition, and Signature Bank.
The yearly stress tests set minimum capital thresholds for banks to be financially stable to pay their shareholders dividends and share buybacks.
The hypothetical stress variables include:
- 36% decline in housing prices.
- 40% decrease in commercial real estate pricing.
- 6.5% increase in U.S. unemployment rates.
The test also includes exploratory analysis that will measure a bank’s susceptibility to risks beyond what’s included in traditional tests. It includes funding stress that affects the repricing of deposits for large banks, specific market fluctuations that are applicable only to the largest and most complex banking systems, and the failure of five hedge funds under different financial market scenarios.
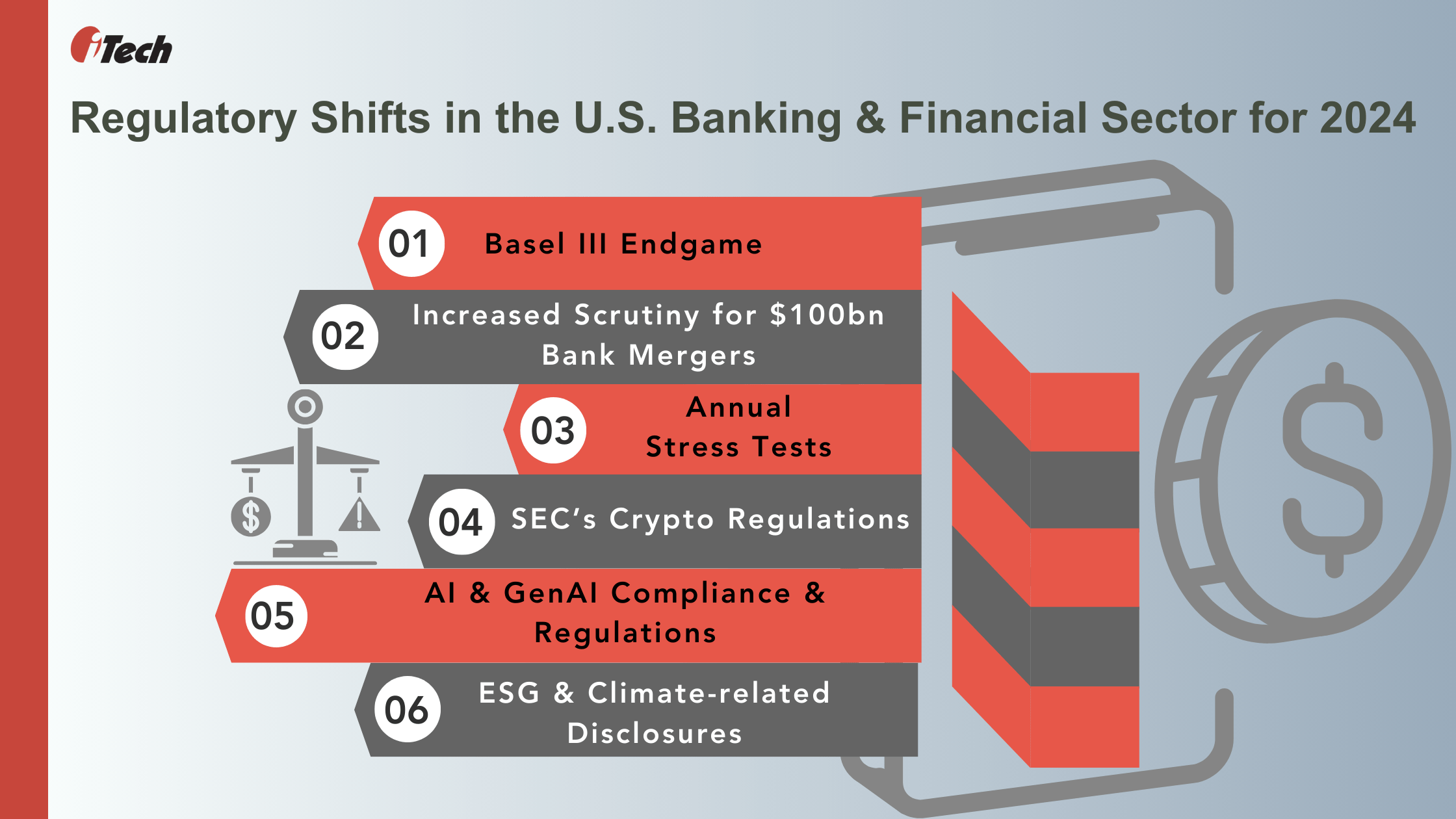
SEC’s Come & Register Approach for Cryptos:
SEC Chair, Gary Gensler asked crypto tokens to be registered with the SEC and comply with its regulations. However, crypto exchanges and firms do not agree with the approach that crypto tokens are securities that must be registered with the SEC. Moreover, in the past the SEC has never allowed any broker-listed or registered exchange to trade cryptos and believes that any registered institution dealing with cryptos cannot trade traditional securities. On January 10, 2024, the commission approved trading and listing of spot bitcoin exchange-traded products.
Gen AI Compliance & Regulation:
AI regulations and compliance apply to the banking industry in a variety of ways. The landmark Executive Order around AI issued by President Biden includes standards around AI safety, best practices for authenticating AI content, and cybersecurity programs to address software vulnerabilities. With the recent buzz around GenAI, Congress introduced the Algorithmic Accountability Act of 2023, targeting the GenAI systems and people impacted by the decisions related to education, credit, and housing.
In addition, the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) and other regulatory agencies issued a statement to enforce current laws to manage AI risks. These regulations provide a high-level understanding of the banking and financial companies’ obligations. However, the recent privacy and data protection laws like CCPA, GDPR, and others will continue to enforce regulatory requirements on banking institutions. SEC’s latest rules remain at the proposal stage. All in all, these developments hint at enhanced bank regulation and supervision to limit the threats of biases from AI use.
ESG & Climate Disclosures:
This year, the U.S. SEC announced final rule on climate disclosures and all actions will go into effect after the elections. Also, states like California passed a climate bill to include Scope 3 emissions for financial service institutions to declare their financial emission. This is said to have a positive impact on the supply chain, driving disclosures outside of the state.
Additionally, some states in the country have also introduced anti-ESG regulation bills, opposing fiduciary duties and penalizing companies, including banking and financial firms, that carry out pro-ESG practices.
Avoid Further Dysfunction with Regulatory Compliance Management
Too many new proposals for bank regulation and supervision are a powerful reminder that interactions of monetary and banking variables on the economy are dynamic. As vulnerabilities pile up for both banking and financial businesses and their customers, regulators and technology providers play a key role in helping firms avoid further dysfunction.
At iTech GRC, we are uniquely positioned as an IBM RegTech partner to access the right experts to analyze the key attributes of your organizations’ regulatory processes and define a practical GRC roadmap implementing OpenPages with Watson.
If you have felt the recent ripples of ever-evolving regulatory frameworks, let’s connect to our team to make the most of OpenPages Regulatory Compliance Management solutions.
