Top Telecom and Network Regulatory Compliance Risks to Watch in 2024

Federal agencies’ landmark regulations, such as the net neutrality, Truth-in-Billing policy, and robocall and texting guidelines, underscore the importance of risk and compliance management for telcos. Like every other industry, the U.S. telecom sector is a part of the GenAI adoption race, and communications services providers (CSPs) are tasked with providing proof of concept. From a technological angle, testing out GenAI opens a doorway to risks such as data governance, data ethics, foundational models, and errors. More risks await as network and telecom providers must ensure data quality and security while sharing it with cloud service providers.
Mounting risks mean compliance violations may occur. However, the silver lining for telcos is the opportunity to discover new ways to stay competitive by delivering on the promise of uninterrupted connectivity and accommodating the latest regulatory and global market demands.
We will uncover diverse risks advancing throughout 2024 and break them down to understand the challenges associated with each one. Meanwhile, your enterprise can explore the OpenPages Policy and Compliance Management module, using iTech GRC’s dedicated risk and compliance advisory team to stay on top of telecom and network regulatory compliance risks.
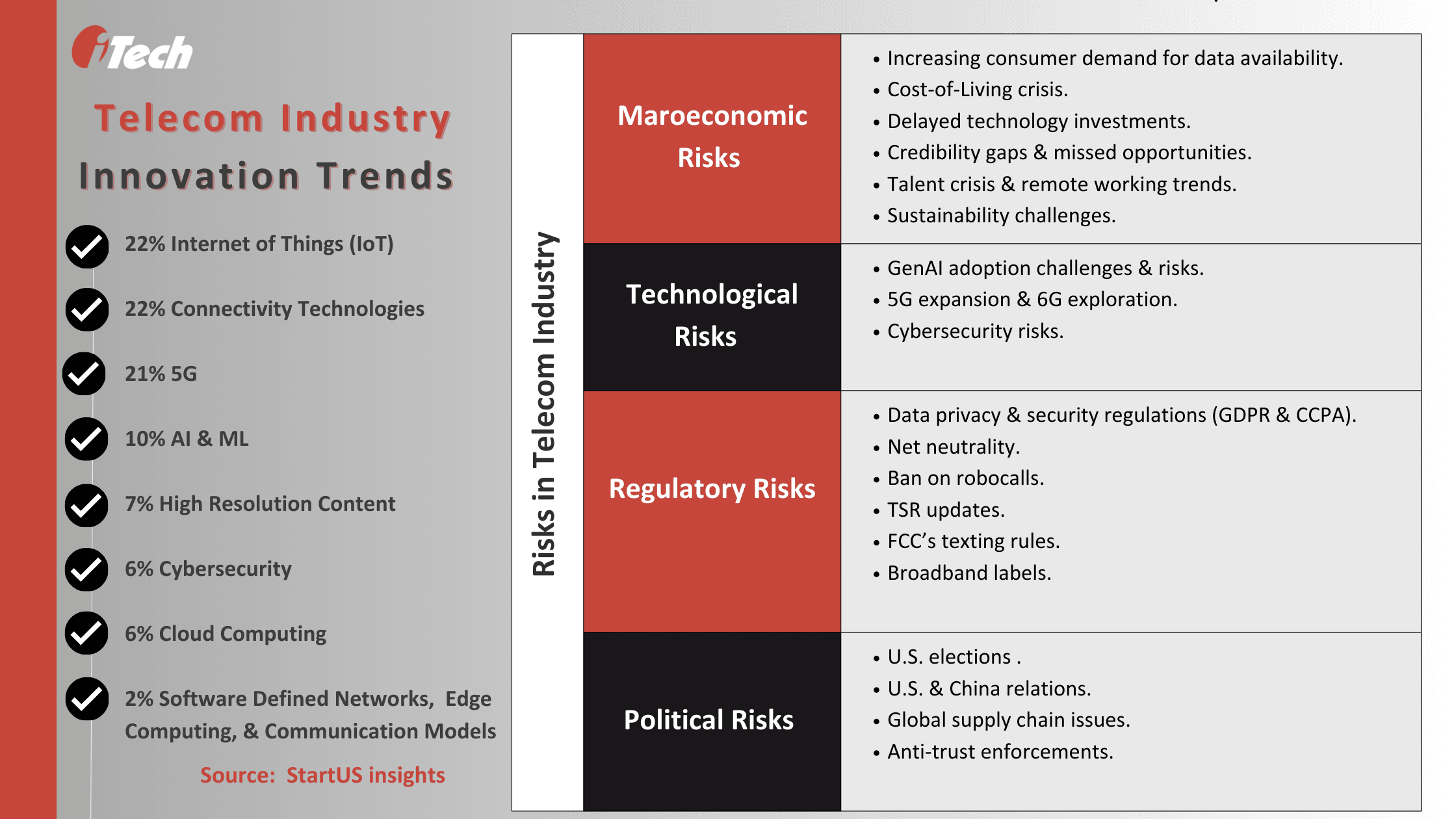
Macroeconomic Risks:
- High Demand for Data Availability: Global data consumption trends by PwC reveal a sharp increase in demand for telecommunication services. This is attributable to consumers’ preference for video data. According to estimates, digitized video content will account for nearly 79% of the 9.7 million PB of data consumed in 2027. The average amount of data consumed between 2023 and 2027 is likely to exceed 2022’s data consumption stats across all categories. Games and developments in the metaverse are also adding to consumers’ data demands. These trends drive telcos to keep up with the demand for high-speed and high-availability networks at any cost while staying alert for outage and latency risks.
- Cost-of-Living Crisis: Stiff competition and cost-of-living crisis are interrelated. They impact the telecom industry as the cost-of-living crisis forces consumers to curd spending on non-essential services like premium plans, streaming services subscriptions, and network packages and seek affordable alternatives. This would reduce profit margins for telecom companies as they are driven to choose a pricing strategy against rising operating costs from energy, network infrastructure, and supply chain management.
- Delayed Investments in Technology: The vicious cycle of consumers’ cost-of-living crisis drives price sensitivity, which discourages buying premium services. The cutback from B2C revenue delays investments to scale 5G projects or fiber-optic networks.
- Credibility Gaps and Missed Opportunities: The EY Reimagining Industry Future study on enterprise executives’ attitudes towards 5G, IoT, and other tech developments reveals that telcos have severe credibility gaps as digital advisors. Even though there are enough opportunities in the enterprise space, telcos have minimal potential to test and leverage new business models. B2B services like security and IoT only account for a proportion of their revenue, so telcos haven’t been able to penetrate newer areas like consulting or software-related services.
- Talent Crisis & Remote Work: In 2023, nearly 55% of telco employers were on a hiring freeze to control costs. The companies also cited risks related to their talent resources, such as retention, attraction, and building next-gen talent. Moreover, telco companies must accommodate 30% of employees who prefer working remotely.
- Sustainability & Climate Change Initiatives: According to the Global Sustainability Barometer study by Ecosystm, involving more than 1,500 technology and business leaders across the globe, organizations believe that sustainability is a strategic imperative but still need an action plan. In the telecom industry, climate-related financial disclosures haven’t increased since 2022. 43% of telecom and tech firms need to disclose their net-zero goals, and 46% need to weigh sustainability in capital allocation sufficiently.
Technological Risks:
- Risks Associated with GenAI Adoption: Among disruptive innovation strategies, GenAI has been the most recent yet significant concern for CSPs. There’s ample concern around managing costs, algorithmic biases and discriminations, and potential vulnerabilities. It drives telcos to engage in rigorous testing to address ethical risks and continuously monitor for the security and explainability of AI and GenAI-powered tools and solutions.
- 5G Expansion & 6G Exploration: 5th-generation mobile networks or 5G projects support the demand for high-speed connectivity and handling large data loads. By 2035, 5G will drive $13 trillion in global economic output. Telco’s capital expenses are influenced by operators rolling out 5G while expanding their fiber infrastructure, cloud migration, and moving to open-source network solutions to support IoT and advanced technology initiatives like AR and VR. The investment pressures add further financial strain on the telecom industry, as businesses need help containing operational costs, efficiency, and additional capacity to make 5G available and explore possibilities for 6G.
- The influx of Security & Privacy Risks: In 2023, almost 74 million telecom customers were affected by data breaches within the first two months. The telecom industry’s physical infrastructure, systems, and networks are critical for national security, maintaining public health, and supporting banking and financial transactions. They are also a soft target for cybercriminal attacks and physical destruction. Telcos must persist with cybersecurity measures to keep their networks, customer data, and infrastructure secure. This requires ample investment in tools for breach and attack prevention from DDoS attacks, malware, phishing, and insider threats.
Regulatory Compliance Risks:
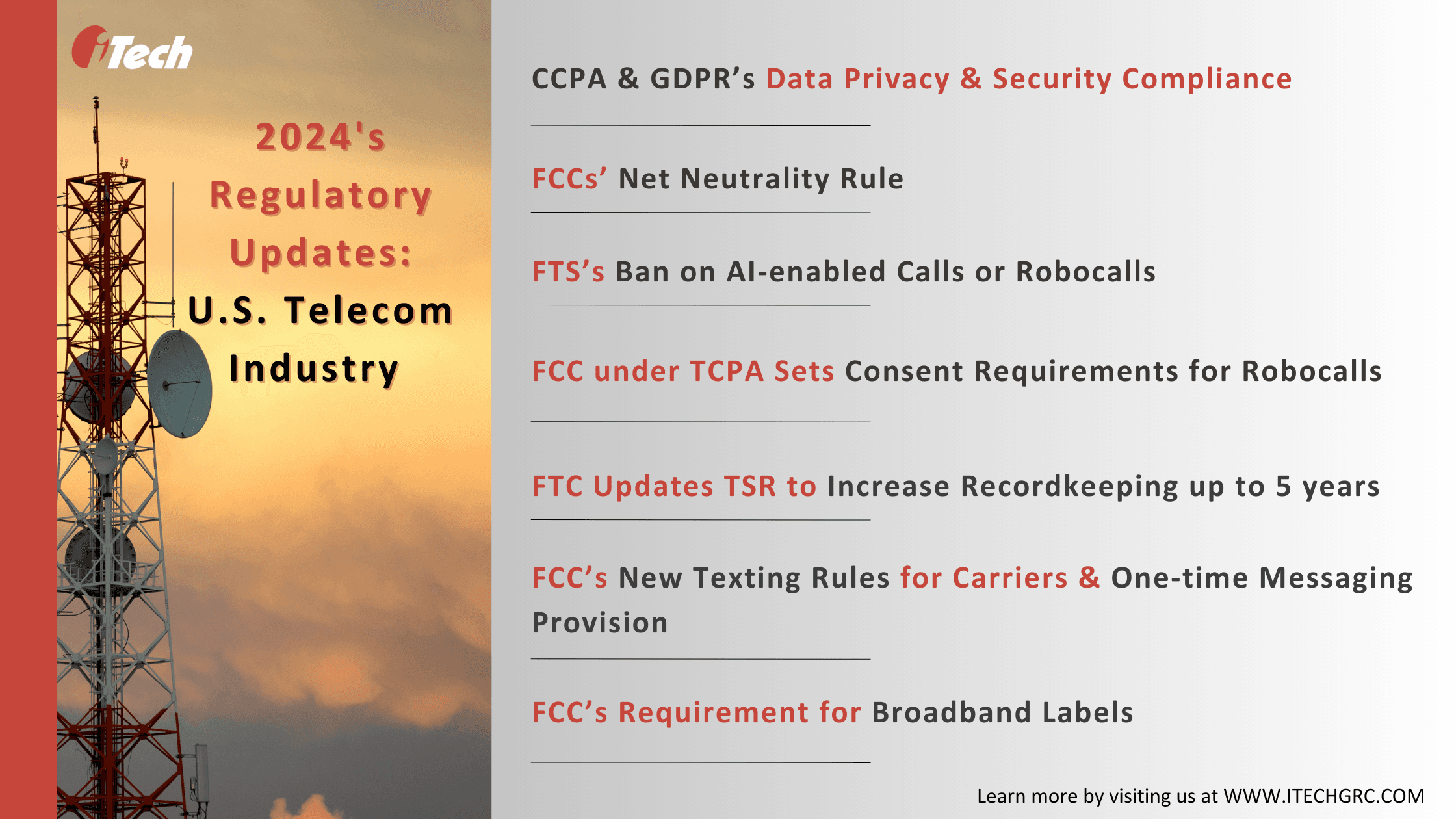
Government and regulatory agencies actively shape telecom companies and their agenda by regulating their competition strategies, protecting consumer interests, and supporting digital initiatives. Nearly 61% of telco leaders believe regulatory compliance risks will impact business performance. There have been recent updates in legal frameworks and policies added to the list of regulatory risks for companies in the telecom ecosystem:
- Data Privacy & Security Regulations: The U.S. telecom industry is subject to regulatory scrutiny regarding how it handles customer data. It must demonstrate compliance with the EU’s GDPR and CCPA to prevent legal penalties and misuse of customers’ sensitive data, such as social security numbers, date of birth, banking information, and more.
- Net Neutrality: The net neutrality principle introduced during the Obama era was finally restored by the Biden administration in 2024 to protect internet users from internet service providers (ISPs) unfair practices like slowing down or blocking competitors’ content, invasion of user privacy, adding hidden fees, etc. Title II of the Federal Communication Commission’s (FFC) net neutrality requires ISPs to ensure affordable, equitable, and safe internet access to all communities. It also imposes strict transparency rules, no paid prioritization, privacy, and a general duty of reasonableness in the open Internet order.
- Ban on Robocalls: The FTC’s recent protection for businesses against telemarketing fraud and AI-enabled scam calls under the Telemarketing Sales Review (TSR) also includes prohibitions on robocalls. The FCC, under the Telephone Consumer Protection Act (TCPA), also requires any AI technology impersonating human voice to satisfy its consent requirements for preventing misuse and fraud by bad actors.
- Telemarketing Sales Rule (TSR) Updates: The FTC’s updates to the TSR include changing recordkeeping requirements from 24 months to five years.
- New Texting Rules: The FCC also added changes to text messaging rules and confirmation for carriers and text message senders. It announced that all mobile wireless providers block illegal messages before September 05, 2024, and allow entities to send one-time messages to users after they revoke consent to receive additional messages.
- Broadband Labels: The FCC’s latest requirement for providers with less than 100,000 subscribers to display broadband labels at the point of sale is modeled after the FDA’s nutrition labels. The rule requires ISPs to share important information about broadband prices, rates, broadband speed, and data allowances.
Political Risks:
- U.S. Elections: The 2024 presidential elections will affect telecom policies. Under democratic leadership, it’s more likely to strengthen net neutrality rules, privacy regulations, and antitrust laws. There will also be stricter regulations over telecom mergers and broadband access. Under Republican leadership, it is more likely to find relaxation on net neutrality, privacy policies, and industry consolidation.
- U.S.-China Relations: Tensions surfacing between the two nations will affect the telecom industry’s use of Chinese technologies and hardware in infrastructure. Already, the U.S. has restrictions on Huawei and ZTE for national security-related reasons. The restriction limits the reach and access to affordable telecom parts and equipment.
- Global Supply Chain Issues: According to research, 85% of telecom operators have suffered project timeline disruptions due to supply chain disruptions. These disruptions are caused by the delay in sourcing new equipment from original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). These delays are responsible for a 30% increase in the cost of network hardware. The impact of global supply chain and semiconductor shortages is slowing down ambitious 5G projects and next-gen network rollouts.
- Antitrust Enforcements: Antitrust enforcement in the telecom industry and increased surveillance of practices and mergers between companies can create roadblocks. Telecom companies will have to prove their credibility with regulatory and government authorities. If they choose to merge for market share and expansion of service portfolio, they are likely to draw regulatory attention under antitrust laws.
Conclusion:
In summary, risks are multivariate in the telecom industry. However, the goal is to protect consumers’ interests and avoid legal consequences for non-compliance. Effective risk management and compliance policy management strengthen telcos’ agility to adapt to shifting regulations and political trends.
Using OpenPages’ Regulatory Compliance Management module, it is easier to have a consolidated overview of regulatory risks, requirements, and interactions. By leveraging the OpenPages Policy Management module, telecom companies can ease the complexities of government and regulatory compliance mandates and automate policy changes as per requirements.
Are you seeking expertise to understand and upgrade your enterprise’s risk management strategies? iTech GRC’s risk and advisory team can help skip the complex maze of compliance risks and adopt procedures to stay current and relevant.
Contact our team today!
